Cloud Computing Consulting
Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage (cloud storage) and computing power, without direct active management by the user.
The term is generally used to describe data centers available to many users over the Internet. Large clouds, predominant today, often have functions distributed over multiple locations from central servers. If the connection to the user is relatively close, it may be designated an edge server.
Clouds may be limited to a single organization (enterprise clouds), or be available to multiple organizations (public cloud).
The term is generally used to describe data centers available to many users over the Internet. Large clouds, predominant today, often have functions distributed over multiple locations from central servers. If the connection to the user is relatively close, it may be designated an edge server.
Clouds may be limited to a single organization (enterprise clouds), or be available to multiple organizations (public cloud).
Cloud Computing Explained
Imagine you're the owner of a small software development firm and you want to scale your business up. However a small team size the unpredictability of demand and limited resources are roadblocks for this expansion. That's when you hear about cloud computing but before investing money into it, you decide to draw up the differences between on-premise and cloud based Computing to make a better decision when it comes to scalability, you pay more for an on-premise Etta and get lesser options to.
Once you've scaled up, it is difficult to scale down and often leads to heavy losses, in terms of infrastructure and maintenance costs cloud computing. On the other hand allows you to pay only for how much you use with much easier and faster. Provisions for scaling up or down next. Let's talk about server storage on-premise systems. Need a lot of space for their servers, notwithstanding the power and maintenance hassles that come with them. On the other hand cloud. In Solutions are offered by cloud service providers, who manage and maintain the server's saving. You both money and space.
Then we have data security on-premise systems offer, less data security. Thanks to a complicated combination of physical and traditional, it security measures, whereas cloud computing systems offer. Much better, security, and lets you avoid having to constantly Monitor and manage security, protocols in the event that a data loss does occur the chance for data recovery. Every with on-premise setups are very small in contrast, cloud computing systems have robust disaster recovery measures in place to ensure faster and easier data recovery.
Finally, we have maintenance on premises systems. Also, require additional teams for hardware and software maintenance loading up the cost by a considerable degree cloud computing systems. On the other hand are maintained by the cloud service providers, reducing your costs and resource allocation substantially. So now thinking that cloud computing is a better option, you decide to take a closer look at what exactly cloud computing is cloud.
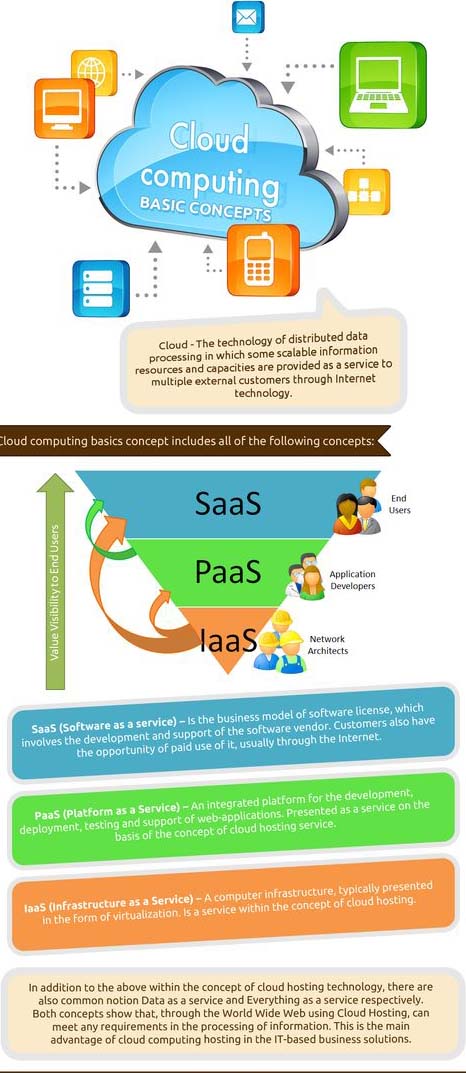
Computing refers to the delivery of on-demand Computing Services, over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. In simpler words, rather than managing files and services on a local storage device. You'll be doing the same over the internet, in a cost-efficient manner, cloud computing has two types of models deployment model, and service model. There are three types of deployment Al's public private and hybrid Cloud.
Imagine you're traveling to work, you've got three options to choose from one. You have buses, which represent public clouds. In this case, the cloud infrastructure is available to the public over the Internet. These are owned by cloud service providers to then you have the option of using your own car. This represents the private cloud with the private Cloud. The cloud infrastructure is exclusively operated by a single Ization. This can be managed by the organization or a third party and finally, you have the option to hail a cab.
This represents the hybrid Cloud. Hybrid cloud is a combination of the functionalities of both public and private clouds. Next, let's have a look at the service models. There are three major service models available es pass and SAS compared to on-premise models where you'll need to manage and maintain every component including applications data. Virtualization and middleware cloud computing. Service models are hassle-free is refers to infrastructure as a service. It is a cloud service model or users get access to basic Computing infrastructure they are. Commonly used by it administrators if your organization requires resources, like storage or virtual machines is is the model for you.
You only have to manage the data runtime middleware applications and the OS. While the rest is handled by the cloud providers. We have pass pass or platform as a service provides Cloud platforms. And runtime environments for developing testing and managing applications, this service model enables users to deploy applications.
Without the need to acquire manage and maintain the related architecture. If your organization is in need of a platform for creating software applications, pass is the model for you pass. Only requires you to handle the applications and the data, the rest of the components like runtime, middleware. Operating systems servers storage and others are handled by the cloud service providers. And finally, we have SAS SAS or software as a service involves cloud services for hosting. And managing your software applications software and Hardware requirements are satisfied by the vendors. So you don't have to manage any of those aspects of the solution. If you'd rather not worried about the hassles of owning any it equipment, the SAS model would be the one to go with with SAS the cloud service.
Handles all components of the solution required by the organization time for a quiz. Now in which of the following deployment models are you as the business responsible for the application data and operating system, one is to pass three SAS for is and pass. Let us know your answer in the comment section below for a chance to win an Amazon, voucher coming back to cloud computing, some of the most popular cloud Computing Services in the market are AWS or Amazon web services, Microsoft Azure, and Google. Cloud platform.
Once you've scaled up, it is difficult to scale down and often leads to heavy losses, in terms of infrastructure and maintenance costs cloud computing. On the other hand allows you to pay only for how much you use with much easier and faster. Provisions for scaling up or down next. Let's talk about server storage on-premise systems. Need a lot of space for their servers, notwithstanding the power and maintenance hassles that come with them. On the other hand cloud. In Solutions are offered by cloud service providers, who manage and maintain the server's saving. You both money and space.
Then we have data security on-premise systems offer, less data security. Thanks to a complicated combination of physical and traditional, it security measures, whereas cloud computing systems offer. Much better, security, and lets you avoid having to constantly Monitor and manage security, protocols in the event that a data loss does occur the chance for data recovery. Every with on-premise setups are very small in contrast, cloud computing systems have robust disaster recovery measures in place to ensure faster and easier data recovery.
Finally, we have maintenance on premises systems. Also, require additional teams for hardware and software maintenance loading up the cost by a considerable degree cloud computing systems. On the other hand are maintained by the cloud service providers, reducing your costs and resource allocation substantially. So now thinking that cloud computing is a better option, you decide to take a closer look at what exactly cloud computing is cloud.
Computing refers to the delivery of on-demand Computing Services, over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. In simpler words, rather than managing files and services on a local storage device. You'll be doing the same over the internet, in a cost-efficient manner, cloud computing has two types of models deployment model, and service model. There are three types of deployment Al's public private and hybrid Cloud.
Imagine you're traveling to work, you've got three options to choose from one. You have buses, which represent public clouds. In this case, the cloud infrastructure is available to the public over the Internet. These are owned by cloud service providers to then you have the option of using your own car. This represents the private cloud with the private Cloud. The cloud infrastructure is exclusively operated by a single Ization. This can be managed by the organization or a third party and finally, you have the option to hail a cab.
This represents the hybrid Cloud. Hybrid cloud is a combination of the functionalities of both public and private clouds. Next, let's have a look at the service models. There are three major service models available es pass and SAS compared to on-premise models where you'll need to manage and maintain every component including applications data. Virtualization and middleware cloud computing. Service models are hassle-free is refers to infrastructure as a service. It is a cloud service model or users get access to basic Computing infrastructure they are. Commonly used by it administrators if your organization requires resources, like storage or virtual machines is is the model for you.
You only have to manage the data runtime middleware applications and the OS. While the rest is handled by the cloud providers. We have pass pass or platform as a service provides Cloud platforms. And runtime environments for developing testing and managing applications, this service model enables users to deploy applications.
Without the need to acquire manage and maintain the related architecture. If your organization is in need of a platform for creating software applications, pass is the model for you pass. Only requires you to handle the applications and the data, the rest of the components like runtime, middleware. Operating systems servers storage and others are handled by the cloud service providers. And finally, we have SAS SAS or software as a service involves cloud services for hosting. And managing your software applications software and Hardware requirements are satisfied by the vendors. So you don't have to manage any of those aspects of the solution. If you'd rather not worried about the hassles of owning any it equipment, the SAS model would be the one to go with with SAS the cloud service.
Handles all components of the solution required by the organization time for a quiz. Now in which of the following deployment models are you as the business responsible for the application data and operating system, one is to pass three SAS for is and pass. Let us know your answer in the comment section below for a chance to win an Amazon, voucher coming back to cloud computing, some of the most popular cloud Computing Services in the market are AWS or Amazon web services, Microsoft Azure, and Google. Cloud platform.